● ARM 프로세서의 구조

Manual에 나와있는 블록도
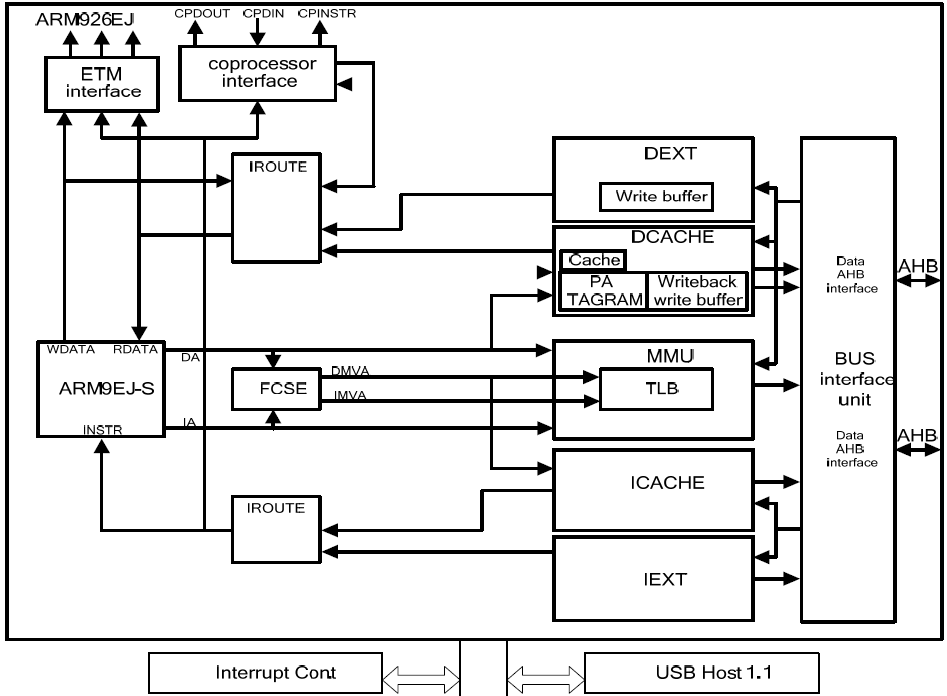
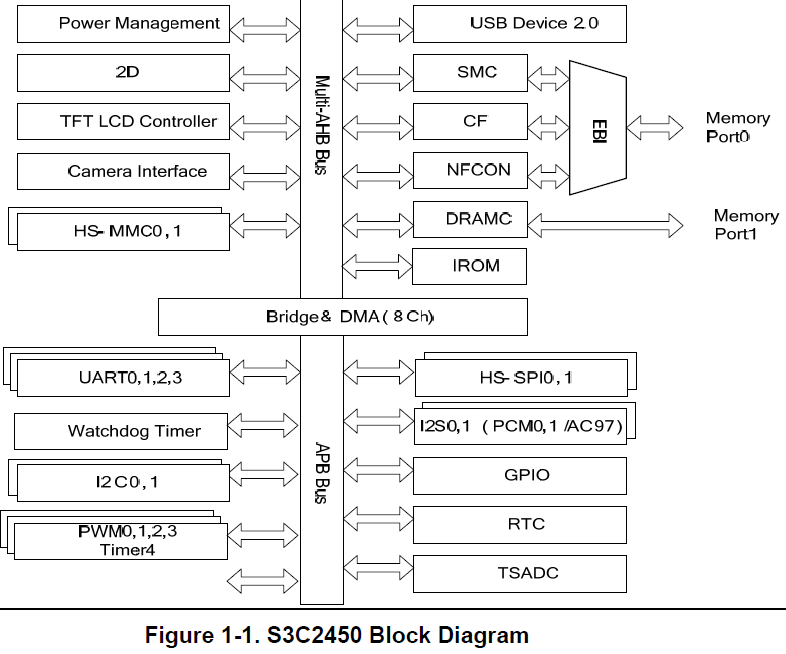
● Cached ARM 프로세서의 제어
▷ CP15 인터페이스를 통해서 제어
- Cache, MPU,or MMU, endian 제어등
▷ Coprocessor Register Transfer 명령
- MRC : Move to Register from Coprocesser :: 내용을 ARM 레지스터로 전송
- MCR : Move to Coprocesser from Register :: ARM 레지스터 내용을 Coprocessor 레지스터로 전송
▷ 참고 자료 : https://blog.naver.com/kazama10/50179092022
[ARM Assembly] MRC, MCR
1. MRC 명령어 - coprocessor 내부의 레지스터를 에서 ARM 레지스터로 읽어들이는 명령어 - MRC{ c...
blog.naver.com
● Cache 메모리
2020/07/28 - [임베디드/IoT 임베디드 SW 개발자 양성과정] - [12일차] 임베디드 시스템 아키텍쳐-개발환경, 아키텍쳐
▷ Cache가 없으면 고속의 cpu가 버스 및 메모리 속도에 의존적이며 낮다.
▷ Cache가 있으면 CPU 주변에 고속의 메모리를 두고 자주 사용되는 명령과 데이터를 저장하여 시스템 성능을 개선한다.

▷ 장점
- 버스의 사용장을 줄여 시스템 성능 향상
- 전력소모를 줄인다.
- 속도가 느린 메모리 시스템의 성능 개선
▷ 성능
- CPU가 데이터나 명령을 읽고자 하는데 cache 내에 원하는 명령이나 데이터가 없으면 -> Cache Miss
- Cache 제어기는 시스템 메모리 장치에서 line 크기 만큼 명령이나 데이터를 읽어 Cache 메모리에 저장(Line Fill)한다.
- Cache Line : Cache가 관리하는 최소한의 데이터 단위.
:: 4 word, 8 word 정도의 크기를 가진다.
▷ Cache Lockdown
- Cache의 일정 부분을 update 되지 않도록 한다.
:: 중요한 명령이나 데이터를 항상 Cache에 있도록 하여 성능 증가 및 보장.
- Cache Fluch 전에는 반드시 Lockdown을 해제하여야 한다.
(*Cache Fluch : Cache line의 data를 0으로 변경하여 초기화하는 작업)

● Write Buffer
▷ Core와 버스의 서로 다른 속도 차 극복
- Core 속도로 write buffer에 데이터를 write
:: write 후 cpu는 다른 작업 처리 가능
- Bus 속도로 write buffer의 내용을 메모리로 write
- write buffer는 FIFO형태(queue)의 구조를 가진다.
▷ Cache와 Write Buffer
▶ Write Through(buffer를 거치지 않을 때)
:: CPU가 특정 주소에 명령이나 데이터를 write하는 경우, 해당하는 명령이나 데이터가 Cache 메모리에 있을 때, Cache메모리와 외부메모리에 모두 쓰기 동작을 한다.
- write buffer를 거치지 않고 메모리에 저장.
▶ Write Back (Cpu가 buffer에 저장하고 돌아온다.)
- CPU가 특정 주소에 명령이나 데이터를 write하는 경우, 해당하는 명령이나 데이터가 Cache 메모리에 있을 때, Cache 메모리에만 쓰기 동작을 하고, 외부의 메모리에는 나중에 기록된다.
- Write Buffer를 사용한다.
● 메모리 관리 유닛(MMU) : 운영체제에 가상 메모리(Virtual Memory) 기능을 제공.
- (메모리 보호(MPU기능) + 메모리 주소 변환) 하기 위해 필요하다.
:: 연속적 물리 주소가 아니어도 CPU는 연속적 주소로 인식하여 메모리 확장 효과
:: 모든 프로세스마다 동일 주소 사용, CPU의 프로세스 관리 용이 및 구현 단순화

▶ MMU의 구성
▷ Tanslation Lookaside Buffer (TLB)
- 최근에 사용된 가상주소를 물리적 주소로 변화하는 정보화 access permission에 대한 정보를 저장하고 있는 일종의 Cache.
▷ Translation Table Walking Logic
- TLB를 업데이트하고 관리하는 기능을 가진 logic
▷ Access Control Logic
▶ Translation Table (명령어와 데이터가 있는 System Memory에 위치!)
▷ Physical 메모리에 있는 translation 정보를 가지고 있는 Table
▷ Level 1 Translation Table
- 4096개의 32 비트 translation table entry
:: 4GB 메모리를 virtual address 1MB단위로 나누어 관리
:: virtual address 비트 [31:20] ( 0x[000]0 0000)
- Physical memory에 대한 1MB section 단위의 address translation 정보와 access control 정보를 가지거나, 레벨 2 table에 대한 주소 정보를 가진다.
▷ Level 2 Translation Table
- 64KB(large page), 4KB(small page), 1KB(tiny page) 단위의 translation table 정보를 가지고 있다.
- 각 translation table에는 address translation 정보와 access control정보를 가진다.
▶ Translation Lookaside Buffer(TLB) (ARM Processor 에 위치!)
▷ 최근에 사용된 가상 주소를 물리적 주소로 변화하는 정보와 접근 허용에 대한 정보를 저장하고 있는 일종의 "Cache"
▷ TLB가 가상 주소에 대한 translation table entry를 가지고 있으면 access control logic이 접근 가능을 판단.
- 접근이 허용되면 가상 주소를 물리적 주소로 변환 후 접근
- 접근의 허용이 안되면 cpu에서 abort 구동
▷ TLB에 가상 주소에 대한 정보가 없으면 translation table walkiong logic에서 table 정보를 physical메모리에서 읽어 TLB 업데이트.
● MMU 실습하기
▷ 가상의 주소와 물리적인 주소를 연결하는 실습.
▷ main문(main.c)
/*=========================*/
#include "my_lib.h"
#include "option.h"
#include "2450addr.h"
#include ".\images\bicycle.h"
void Main(void)
{
int i;
Uart_Init(115200);
/*
* ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
* FROM HERE WE WILL TEST MMU
*/
#if 1 /* MMU INIT */
Uart_Printf("\nInitialize MMU..\n");
/*
* Initialize MMU
* The MMU initialize routine was implemented at libc.c
*/
MMU_Init();
#else
Uart_Printf("No-MMU..\n");
#endif
#if 1
{
volatile unsigned long *value;
value = (volatile unsigned long *)0x33000000;
*value = 0x0;
unsigned int result;
/*
* EXERCISE TODO : please compare the each cases below:
* 1. disable Cache, Write Buffer of TEXT(명령어)/DATA and TEST sections and measure it.
* 2. enable Cache, Write Buffer of TEXT/DATA sections,
* disable Cache, Write Buffer of TEST and measure it.
* 3. enable Cache, Write Buffer of TEXT/DATA and TEST area and measure it.
*/
Uart_Printf("Performance measure start ..\n");
start_timer0(); /* start timer */
for (i=0;i<0x50000;i++)
*value = *value + 1; /* test */
result = time(); /* get time lap */
stop_timer0(); /* stop timer */
Uart_Printf("Time spend for testing 0x%x.\n", result);
}
#endif
Uart_Printf("MMU Test End\n");
Uart_Send_String("\n\n");
#if 1
/* Frame Buffer Access Test */
{
Graphic_Init( );
Lcd_Draw_BMP(0, 0, bicycle);
}
#endif
}▷ mmu를 초기화 한 뒤, value 변수의 값을 0x50000번 1씩 증가시켜본다.
▶ mmu초기화 함수 MMU_Init.c (lib.c 파일 내부)
void MMU_Init(void)
{
unsigned long i,j;
//========================== IMPORTANT NOTE =========================
//The current stack and code area can't be re-mapped in this routine.
//If you want memory map mapped freely, your own sophiscated MMU
//initialization code is needed.
//===================================================================
MMU_DisableDCache();
MMU_DisableICache();
//If write-back is used,the DCache should be cleared.
for(i=0;i<64;i++)
for(j=0;j<8;j++)
MMU_CleanInvalidateDCacheIndex((i<<26)|(j<<5));
MMU_InvalidateICache();
MMU_DisableMMU();
MMU_InvalidateTLB();
/* MMU_SetMTT(int vaddrStart,int vaddrEnd,int paddrStart,int attr) */
MMU_SetMTT(0x00000000,0x07f00000,0x00000000,RW_NCNB); //bank0 C와 B비트 off
MMU_SetMTT(0x08000000,0x0ff00000,0x08000000,RW_NCNB); //bank1
MMU_SetMTT(0x10000000,0x17f00000,0x10000000,RW_NCNB); //bank2
MMU_SetMTT(0x18000000,0x1ff00000,0x18000000,RW_NCNB); //bank3
MMU_SetMTT(0x20000000,0x27f00000,0x20000000,RW_NCNB); //bank4
MMU_SetMTT(0x28000000,0x2ff00000,0x28000000,RW_NCNB); //bank5
/*
* USER WILL TEST WITH BANK 6
* the each attribute value such as RW_CB, RW_NCNB, .... was decleared on libc.h
*
* 1. EXERCISE TODO: Please IMPLEMENT MMU_SetMTT function
*/
MMU_SetMTT(0x30000000,0x31f00000,0x30000000,RW_CB);//캐시 on/off설정이 아님. 캐시 쓸건지 안쓸건지 설정임. //bank6-1, TEXT/DATA
MMU_SetMTT(0x32000000,0x33e00000,0x32000000,RW_CB); //bank6-2, TEST DATA,LCD FrameBuffer
MMU_SetMTT(0x33f00000,0x33f00000,0x33f00000,RW_CB); //bank6-3
MMU_SetMTT(0x38000000,0x3ff00000,0x38000000,RW_NCNB); //bank7
MMU_SetMTT(0x40000000,0x5af00000,0x40000000,RW_NCNB); //SFR+StepSram
MMU_SetMTT(0x5b000000,0xfff00000,0x5b000000,RW_FAULT);//not used
/*
* 2. EXERCISE TODO: Please IMPLEMENT MMU_SetTTBase function : libs.S
*/
MMU_SetTTBase(_MMUTT_STARTADDRESS); //translation table 시작 주소
/* DOMAIN1: no_access, DOMAIN0,2~15=client(AP is checked) */
MMU_SetDomain(0x55555550|DOMAIN1_ATTR|DOMAIN0_ATTR);
MMU_SetProcessId(0x0);
MMU_EnableAlignFault();
/*
* 3. EXERCISE TODO: Please IMPLEMENT MMU_EnableMMU,MMU_EnableICache and MMU_EnableDCache
* : libs.S
*/
MMU_EnableMMU();
MMU_EnableICache(); //캐시 킴
MMU_EnableDCache(); /* IMPORTANT : DCache should be turned on after MMU is turned on. */
}
/*
* void MMU_SetMTT(int vaddrStart,int vaddrEnd,int paddrStart,int attr)
* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Attribute : RW_CB,RW_CNB,RW_NCNB,RW_FAULT
*/
void MMU_SetMTT(int vaddrStart,int vaddrEnd,int paddrStart,int attr)
{
unsigned long *pTT;
int i,nSec;
/*
* 1. EXERCISE TODO: Get Translation Table base address on Physical memory
* Translation table held each 1 word translation descriptor for each 1MB section
* The Level 1 translation descript location for each 1M section can be calcurated
* from Translation Table Base address and virtual address
*
* The variable for actual translation descriptor location : pTT
* MMU Translation Table Base Address : _MMUTT_STARTADDRESS
* Address bit [31:20] specify M byte address
*/
pTT=(unsigned long *) _MMUTT_STARTADDRESS +(vaddrStart>>20); //포인터 변수에 가상의 주소를 저장
/*
* 2. EXERCISE TODO: We must configure each 1M section descriptor
* So, we must get a number of section from start virtual address (vaddrStart)
* to end of virtual address (vaddrEnd)
* The number of scetion : nSec
*/
nSec=(vaddrEnd>>20)-(vaddrStart>>20);
for(i=0;i<=nSec;i++)
{
/*
* 3. EXERCISE TODO: We must write down physical address and attribute information to
* each section descriptor
* Section descriptor location : *pTT
* Configuration Value : (physical address information) | (attribute)
* The physical address information was held from address bit 20 (1M byte address)
*/
*pTT++ = (((paddrStart>>20)+i)<<20) | attr ; //포인터 참조하여 가상의 주소안의 데이터로 물리적인 주소를 넣는다. 넣고 끝. 이제 가상주소의 안에 있는 데이터는 물리주소이다.
}
}
★이 함수에서 눈여겨볼 부분은 여기이다.
* MMU Translation Table Base Address : _MMUTT_STARTADDRESS
* Address bit [31:20] specify M byte address
*/
pTT=(unsigned long *) _MMUTT_STARTADDRESS +(vaddrStart>>20); //포인터 변수에 가상의 주소를 저장
/*
* 2. EXERCISE TODO: We must configure each 1M section descriptor
* So, we must get a number of section from start virtual address (vaddrStart)
* to end of virtual address (vaddrEnd)
* The number of scetion : nSec
*/
nSec=(vaddrEnd>>20)-(vaddrStart>>20);
for(i=0;i<=nSec;i++)
{
/*
* 3. EXERCISE TODO: We must write down physical address and attribute information to
* each section descriptor
* Section descriptor location : *pTT
* Configuration Value : (physical address information) | (attribute)
* The physical address information was held from address bit 20 (1M byte address)
*/
*pTT++ = (((paddrStart>>20)+i)<<20) | attr ; //포인터 참조하여 가상의 주소안의 데이터로 물리적인 주소를 넣는다. 넣고 끝. 이제 가상주소의 안에 있는 데이터는 물리주소이다.
☆ 대략 진행
1) 가상의 주소 [31:20] (3byte)인 Translation table 의 기본(base) 주소를 설정한다.
2) 가상의 주소를 포인터 변수의 값으로 저장한다.
3) 포인터의 접근으로 가상의 주소 안에 [물리적인 주소 값]를 데이터로 넣는다.
가상의 주소를 간접 참조 연산으로 접근하면 물리적 주소로 접근할 수 있다.
결국 포인터를 잘 활용한 것!!!!!!
corprocessor의 P15인터페이스를 활용해서 캐시와 버퍼 비트를 켜거나 끌 수 있다.
이 부분의 어셈블리 함수 부분은 생략! (libs.S 에 저장되어 있다.)

@@ 참고하기
http://recipes.egloos.com/5170809
Cache, Cash?
Cache라는 건 뭡니까? Cash가 드는 넘 이죠. 흐흐. Cache라는 건 교활한 놈이에요. 돈 잡아 먹는 기계죠. 왜냐! 느린 Memory와 빠른 CPU사이에 장난을 쳐서 마치 빠른 것처럼 만들어 주는 사기꾼인 거죠. �
recipes.egloos.com
http://recipes.egloos.com/5232056
MMU (Memory Management Unit)
MMU는 CPU의 Memory 주소를 감쪽같이 속이는 거짓말쟁이에요. MMU는 표현하고 행동해요. CPU가 Memory를 Access할 때 마다 주소를 속인답니다. 주소를 속여서 어떻게 하느냐, Physical Address와 Virtual Address (Lo
recipes.egloos.com
* 개인적인 학습 목적으로 작성한 글이기에 내용에 잘못된 정보가 있을 수 있습니다.
'임베디드 개발(before) > IoT 임베디드 SW 개발자 양성과정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [31일차] ARM 프로세서 이해 및 활용 (부트코드 작성, 소프트웨어 최적화, LED 실습) (0) | 2020.08.24 |
|---|---|
| [30일차] ARM 프로세서 이해 및 활용(AMBA BUS, Clock, Power, Exception Handling) (0) | 2020.08.22 |
| [28일차] ARM 프로세서 이해 및 활용(ARM 프로세서의 명령어) (0) | 2020.08.20 |
| [27일차] ARM 프로세서 이해 및 활용 (Program Status Register (PSR), Exception) (0) | 2020.08.19 |
| [26일차] ARM 프로세서 이해 및 활용 (임베디드 시스템의 구조, ARM Architecture 전반적인 구조) (0) | 2020.08.18 |